Generating Akamai API Credentials
Before we can use Terraform with Akamai, we need to set up API credentials. These credentials will allow Terraform to interact with Akamai's Property Manager and Security services.
Steps to Create Akamai API Credentials
- Log in to the Akamai Control Center (opens in a new tab).
- Navigate to "Identity & Access" → "API Users & Keys".
- Click on "Create API Client".
- Under "Select API client type" make sure "Myself" is selected on the left, and you choose the "Advanced" option
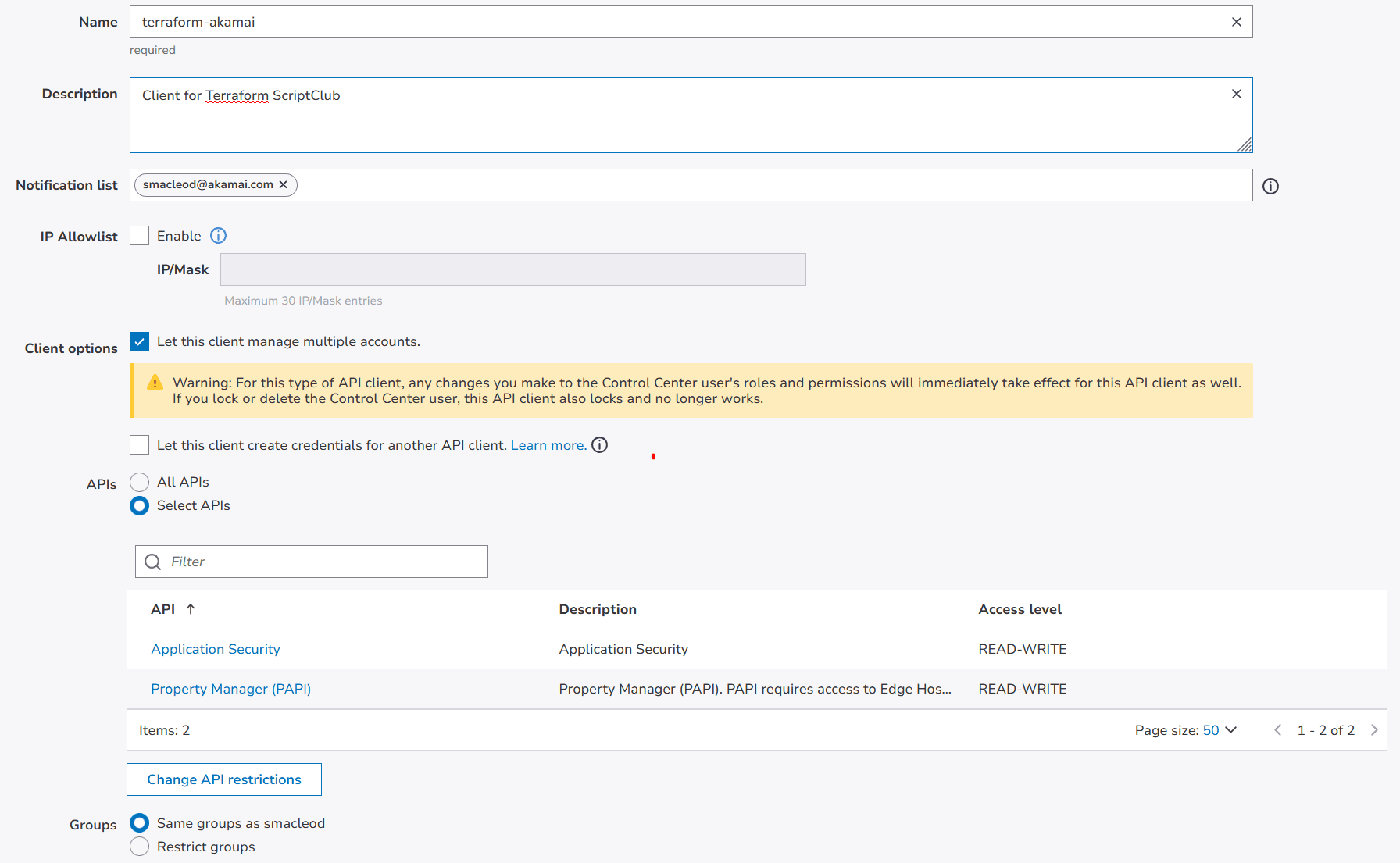
- Fill in the form:
- Name: Choose a descriptive name (e.g., "Terraform-Akamai")
- Description: Briefly describe the purpose (e.g., "API client for Terraform automation")
- Make sure IP Allowlist is unchecked
- Check the box for "Let this client manage multiple accounts"
- Uncheck the box for "Let this client create credentials for another API client"
- Check the Select APIs option, and in the popup select at least these two APIs:
- Property Manager API (PAPI) : read/write
- Application Security (not the internal version, if this is available): read/write
- Under groups, leave the default ("Same groups as |username|") selected
- Click "Create API Client".
- In the next screen click "Download API Client"

Important: After creation, you'll see the client secret and other credentials. Download or copy these immediately—you won't be able to access the client secret again.
Understanding Your Akamai API Credentials
You'll receive four pieces of information:
- Client Token
- Client Secret
- Access Token
- Base URL
All of these are required to authenticate your API requests to Akamai.
Using Akamai Credentials with Terraform
When you're working with more than one account, move between them using an account switch key with an API client enabled to manage multiple accounts. If you're not working with more than one account disregard the AKAMAI_ACCOUNT_KEY and account_key below.
To use these credentials with Terraform, you can set them as environment variables:
Mac / Linux
export AKAMAI_CLIENT_SECRET="your_client_secret"
export AKAMAI_HOST="your_base_url"
export AKAMAI_ACCESS_TOKEN="your_access_token"
export AKAMAI_CLIENT_TOKEN="your_client_token"
export AKAMAI_ACCOUNT_KEY="your_account_id"Windows
$env:AKAMAI_CLIENT_SECRET = "your_client_secret"
$env:AKAMAI_HOST = "your_base_url"
$env:AKAMAI_ACCESS_TOKEN = "your_access_token"
$env:AKAMAI_CLIENT_TOKEN = "your_client_token"
$env:AKAMAI_ACCOUNT_KEY = "your_account_id"Alternatively, you can use an .edgerc file, which is a common way to store Akamai credentials:
- Create a file named .edgerc in your home directory.
- Add the following content, changing the section header to something other than
defaultif you are adding an additional section:
[default]
client_secret = your_client_secret
host = your_base_url
access_token = your_access_token
client_token = your_client_token
account_key = you_account_idThe .edgerc method will be used for the examples and exercises in this course.
Note: If you use account-switching, it is common practice to have multiple sections in your .edgerc file where the 4 core elements (
host,access_token,client_tokenandclient_secret) are the same, but theaccount_keydiffers. This allows you to simply override theconfig_sectionvariable in your terraform to switch between accounts.
Best Practices for Akamai API Credential Security
- Never share your API credentials or commit them to your Git repository.
- Use environment variables or the .edgerc file to manage your credentials securely.
- Regularly rotate your API credentials, especially if you suspect they might have been compromised.
- Only grant the necessary permissions to your API client.
Next Steps
With your Akamai API credentials set up, you're ready to start using Terraform to manage Akamai resources. In the next section, we'll begin configuring Terraform to work with Akamai Property Manager and Security services.